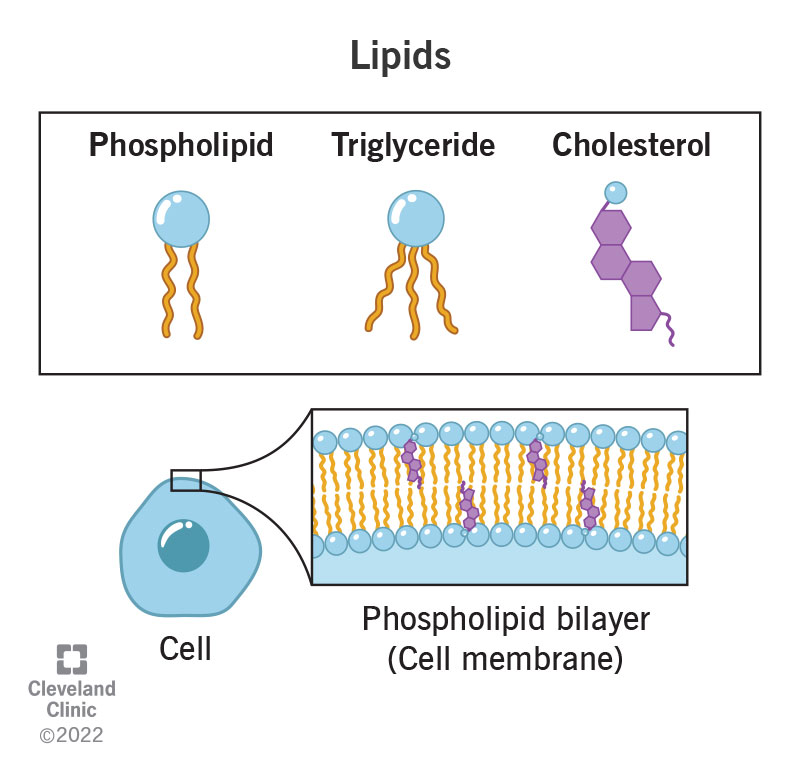
Lipids Drawing
Lipids Drawing - Web lipid diagrams & properties. Web lipids tend to be hydrophobic, nonpolar, and made up mostly of hydrocarbon chains, though there are some variations on this, which we'll explore below. Web this biochemistry video tutorial focuses on lipids. There are three main types of lipids: There are three main types of lipids: Draw a cartoon showing how cholesterol might fit into a bilayer. As we saw with proteins, lipid structure mediates their function. Web from a more molecular perspective, lipids can act as cofactors for enzymes, pigments, antioxidants, and water repellents. So let's probe their structures. This molecule has many biological functions. Fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general formula \(\ce{ch_3(ch_2)_{n}cooh}\), where \(n\) usually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an. On this page, we’ll learn about the structures of these three types of lipids, as well as their functions in the body and where you can find them. These fatty acids have long hydrocarbon ‘tails’. Fatty acyls,. Web lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. Most natural waxes are mixtures of such esters. There are three main types of lipids: Fat cells from white adipose tissue. Triglycerides are a form of lipid. Lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. Draw a cartoon showing how cholesterol might fit into a bilayer. As shown in the diagram above, most lipids are classified as esters or amides of fatty acids. Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed of hydrocarbon. Lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. Web lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. Web a lipid is generally considered to be any molecule that is insoluble in water and soluble. Fats have glycerol in addition to three fatty acids. Fat cells from white adipose tissue. Web lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. An example, cholesterol, is shown below. Web the lipid maps website currently contains a. Waxes, steroids, phospholipids, and fats are the most common types of lipid groups. There are three main types of lipids: Examples of such solvents include acetone and ether. Web you are now able to visualise 3d models of the lipids in lmsd. Web this biochemistry video tutorial focuses on lipids. As we saw with proteins, lipid structure mediates their function. As shown in the diagram above, most lipids are classified as esters or amides of fatty acids. There are three main types of lipids: Biological lipids usually refer to a broad grouping of naturally occurring molecules which includes fatty acids, waxes, eicosanoids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, sphingolipids, sterols, terpenes, prenols.. Web from a more molecular perspective, lipids can act as cofactors for enzymes, pigments, antioxidants, and water repellents. Learn more about the structure, types, and functions of lipids in this article. There are three main types of lipids: Web there are many other different types of lipids. Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed of hydrocarbon chains. Web lipids, as a class of compounds, are insoluble in water but are soluble in other organic solvents. Structures are rendered with javascript / ketcher and may be saved as molfiles. The different varieties of lipids have different structures, and correspondingly diverse roles in organisms. I'm almost done right over here. Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed. Web lipids, as a class of compounds, are insoluble in water but are soluble in other organic solvents. You can fully control the rotation and scaling of the model with your mouse to alter the view point. Fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general formula \(\ce{ch_3(ch_2)_{n}cooh}\), where \(n\) usually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an.. Most natural waxes are mixtures of such esters. Fat cells from white adipose tissue. It is often found in lipid bilayers. So let's probe their structures. Web the lipid maps website currently contains a suite of structure drawing tools for the following lipid categories: Web online versions of the structure drawing tools for fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, and sterols are available in the tools section of the lipid maps website. Examples of such solvents include acetone and ether. Web from a more molecular perspective, lipids can act as cofactors for enzymes, pigments, antioxidants, and water repellents. Learn more about the structure, types, and functions of lipids in this article. They are made up of one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached to it. This molecule has many biological functions. Fats have glycerol in addition to three fatty acids. Web lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. Web lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body. Structures are rendered with javascript / ketcher and may be saved as molfiles. These fatty acids have long hydrocarbon ‘tails’.2.8 Lipids Biology LibreTexts
A schematic drawing of coarsegrained model of lipid molecule. The
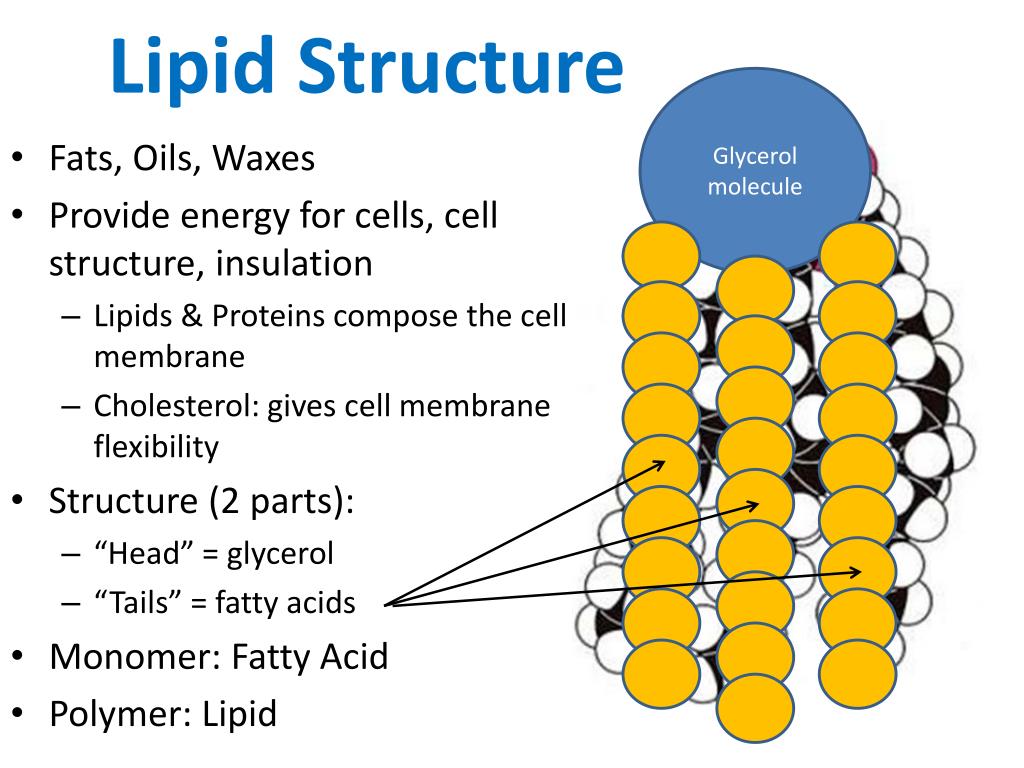
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6999007

Lipid Structure Drawing Sketch Template Thats Chemsketch Alll Sketch
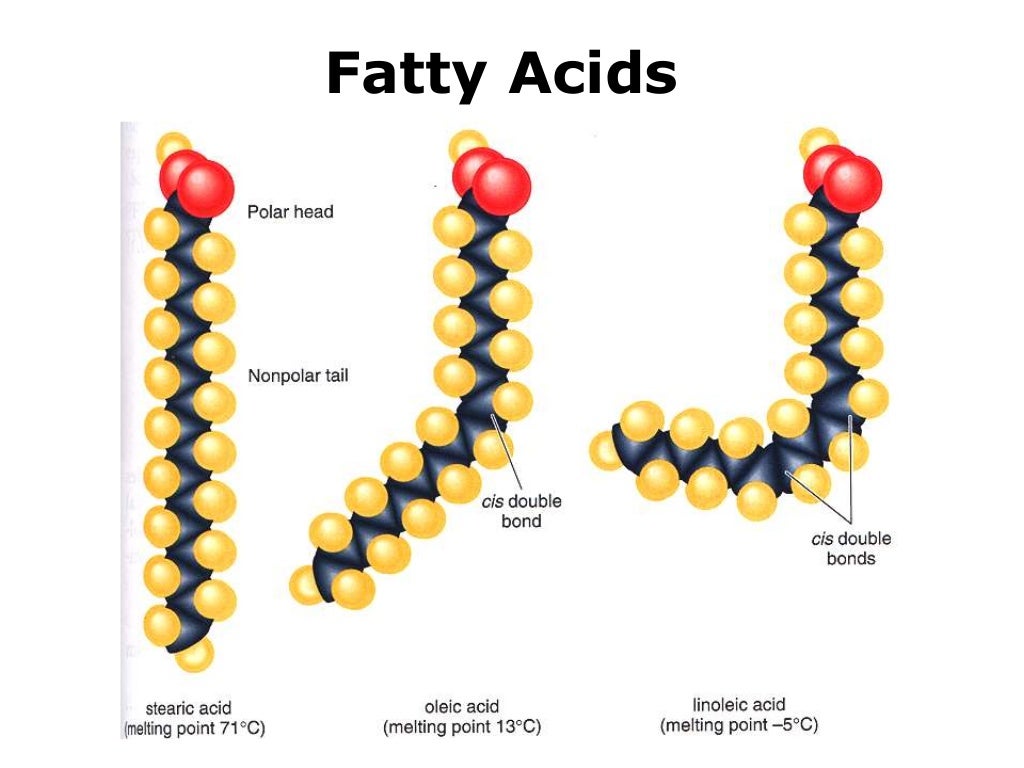
Lipids Chemistry Structure & Function
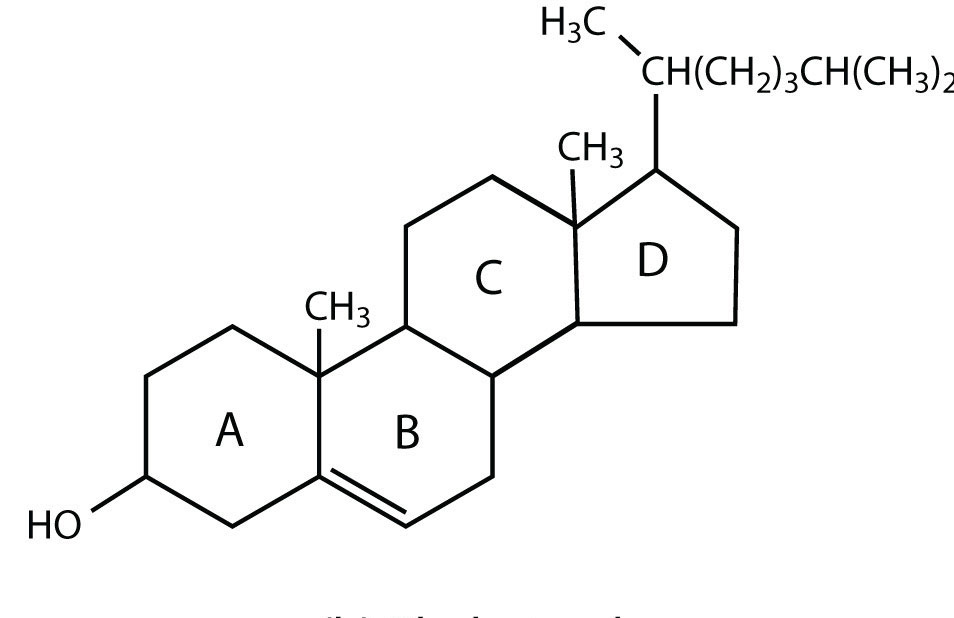
Draw Structure Of Lipid
Chemical Structure Of Lipids
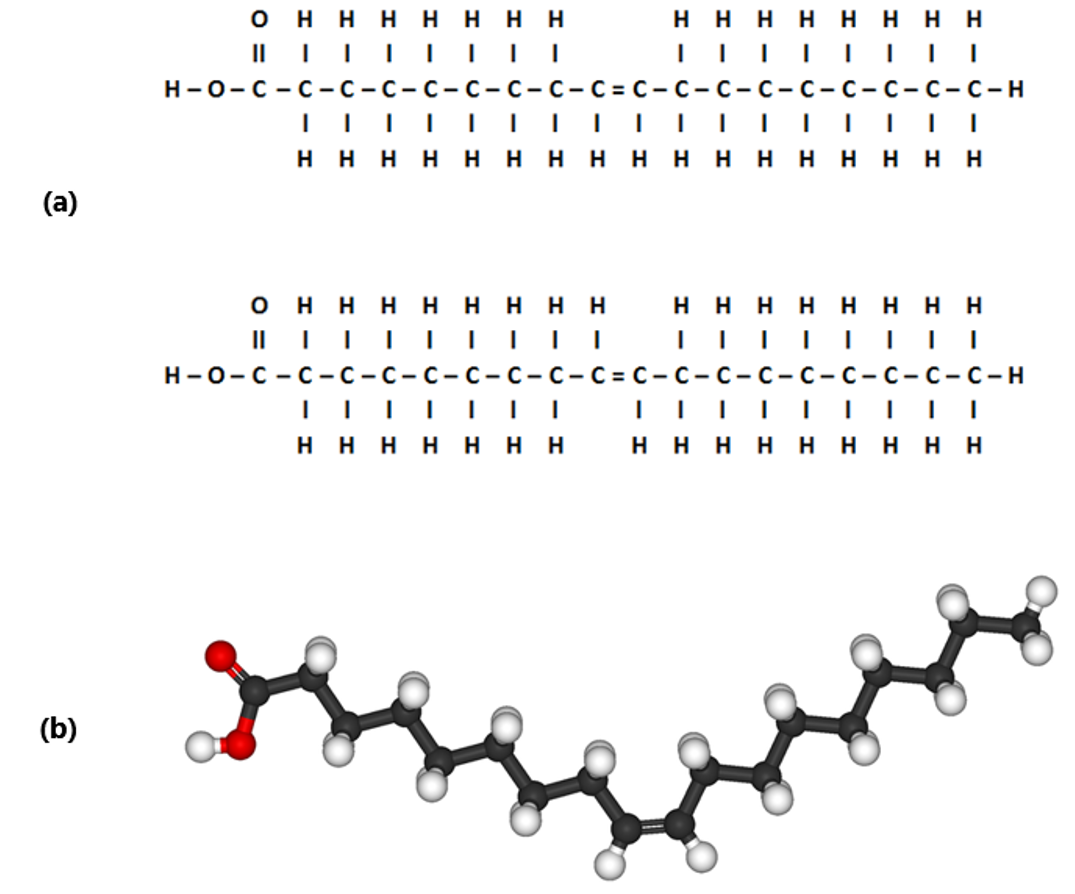
Lipids

Phospholipid or phosphatides lipids head and tail structure outline

Lipids Biology for NonMajors I
Fatty Acyls, Glycerolipids, Glycerophospholipids, Cardiolipins, Sphingolipids, Sterols, And Sphingolipid Glycans.
Organisms Use Lipids To Store Energy, But Lipids Have Other Important Roles As Well.
Biological Lipids Usually Refer To A Broad Grouping Of Naturally Occurring Molecules Which Includes Fatty Acids, Waxes, Eicosanoids, Monoglycerides, Diglycerides, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Sphingolipids, Sterols, Terpenes, Prenols.
Fatty Acyls, Glycerolipids, Glycerophospholipids, Cardiolipins, Sphingolipids And Sterols.
Related Post: