Endocytosis Drawing
Endocytosis Drawing - Web in endocytosis, the cell engulfs some of its extracellular fluid (ecf) including material dissolved or suspended in it. The receptor and coat proteins are clearly visible as larger structures on the. Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: Through this method, cells acquire nutrients required for growth and reproduction. Web the different types of endocytosis: Medical illustration depicting immune system interaction at cellular level. Exocytosis provides the opposite function and pushes molecules out of the cell. In order for endocytosis to occur, substances must be enclosed within a vesicle formed from the cell (plasma) membrane. Web endocytosis, the process of cellular ingestion, may have been the driving force behind evolution of the eucaryotic cell (de duve 2007). Moreover, it plays an important role in dead cell clearance and defense against external microbes. Vesicle, coated vesicle, and phagosome. Pinocytosis (cell drinking) describes the internalization of extracellular fluid and small macromolecules by means of small vesicles. Web it is important to recognize that most endocytosis inhibitors are working on multiple pathways (table 1), which makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the endocytic pathways. Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves. Endocytosis and exocytosis are used by all cells to transport molecules that cannot pass through the membrane passively. In this process, the material to be ingested is progressively enclosed by. Endocytosis ( endo = internal, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a general term for the various types of active transport that move particles into a cell by enclosing them in. Endocytosis and exocytosis are used by all cells to transport molecules that cannot pass through the membrane passively. Web it is important to recognize that most endocytosis inhibitors are working on multiple pathways (table 1), which makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the endocytic pathways. Vector illustration variations of endocytosis: Endocytosis is a type of active transport that. Web endocytosis is a critical process for cell growth and viability. Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: Phagocytosis is also known as cell eating. Web endocytosis is the process of actively transporting molecules into the cell by engulfing it with its membrane. Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of. Vector illustration variations of endocytosis: Web it is important to recognize that most endocytosis inhibitors are working on multiple pathways (table 1), which makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the endocytic pathways. Pinocytosis (cell drinking) describes the internalization of extracellular fluid and small macromolecules by means of small vesicles. Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: Acquiring. Pinocytosis (cell drinking) describes the internalization of extracellular fluid and small macromolecules by means of small vesicles. There are variations of endocytosis, but all follow the same basic process. Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell. The plasma membrane of the cell invaginates,. Vector illustration variations of endocytosis: Web endocytosis is a critical process for cell growth and viability. The routes that lead inward from the cell surface to lysosomes start with the process of endocytosis, by which cells take up macromolecules, particulate substances, and, in specialized cases, even other cells. Web endocytosis is the process of bringing substances inside a cell from. Web the different types of endocytosis: Web endocytosis is the process of bringing substances inside a cell from the external environment with the help of the cell membrane. The membrane folds over the substance and it becomes completely enclosed by the membrane. Vesicle, coated vesicle, and phagosome. Endocytosis and exocytosis are used by all cells to transport molecules that cannot. Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane. The plasma membrane of the cell invaginates, forming a pocket around the target particle. Acquiring the ability to internalize macromolecules and digest them intracellularly would have allowed primordial cells to move out from their food sources and pursue a. Vesicle, coated vesicle, and phagosome. Web endocytosis, the process of cellular ingestion, may have been the driving force behind evolution of the eucaryotic cell (de duve 2007). The carrier and channel proteins discussed in the preceding section transport small molecules through the phospholipid bilayer. Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing. Web transport into the cell from the plasma membrane: There are different variations of endocytosis, but all share a common characteristic: Through this method, cells acquire nutrients required for growth and reproduction. There is a quick trick for drawing endocy. This video shows you how to draw simplified cell membrane in powerpoint for your science figures. Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: The membrane folds over the substance and it becomes completely enclosed by the membrane. Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane. Acquiring the ability to internalize macromolecules and digest them intracellularly would have allowed primordial cells to move out from their food sources and pursue a predatory existence; Pinocytosis (cell drinking) describes the internalization of extracellular fluid and small macromolecules by means of small vesicles. Eukaryotic cells are also able to take up macromolecules and particles from the surrounding medium by a distinct process called endocytosis. Web endocytosis is a critical process for cell growth and viability. Web endocytosis is the process of bringing substances inside a cell from the external environment with the help of the cell membrane. Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell. The carrier and channel proteins discussed in the preceding section transport small molecules through the phospholipid bilayer. Phagocytosis is also known as cell eating.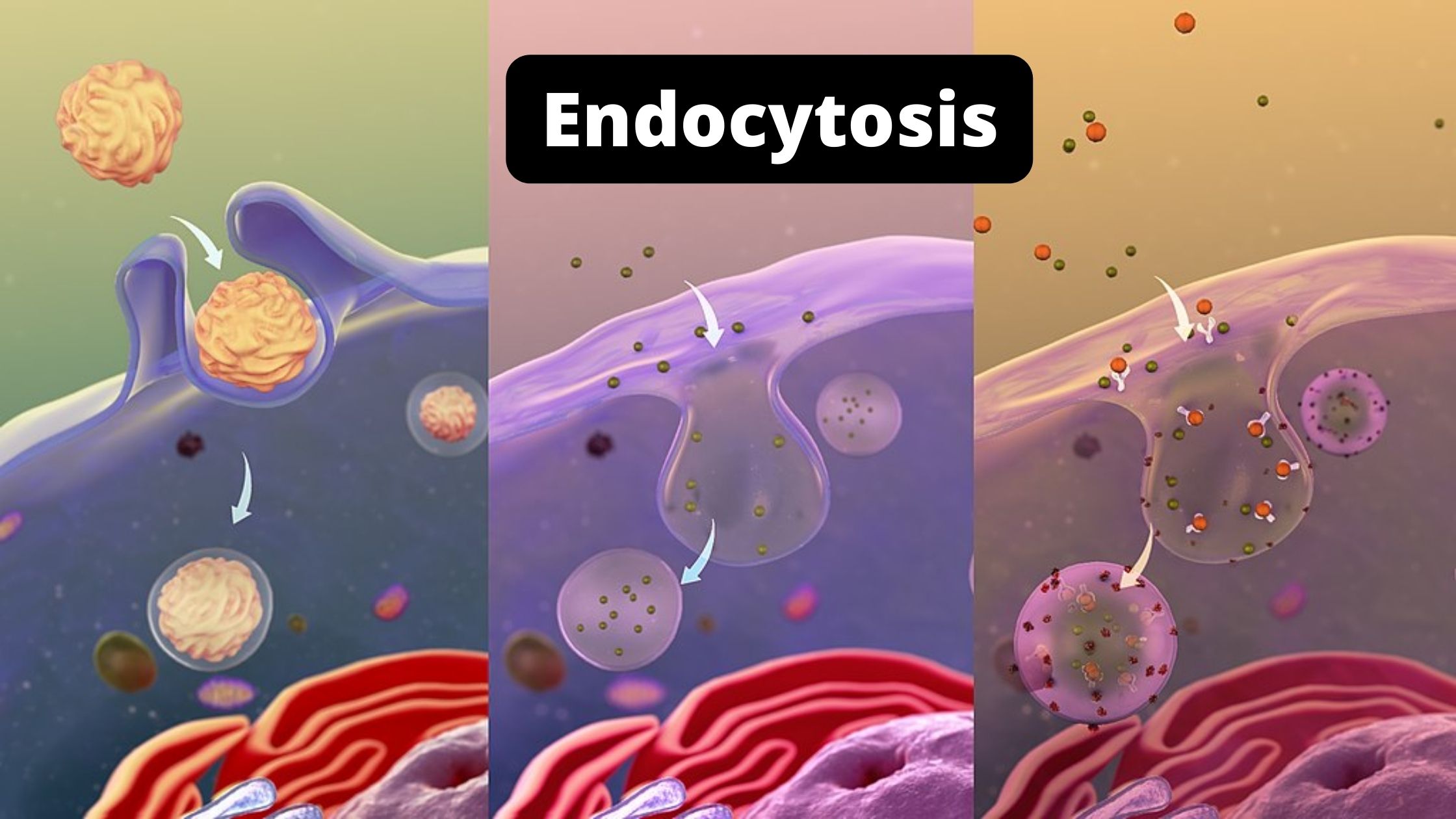
Endocytosis definition, types and Steps.

illustration of Healthcare and Medical education drawing chart of

Endocytosis biology Britannica
/endocytosis-5ad64d57c0647100386364bb.jpg)
A Definition of Endocytosis With Steps and Types
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis_pinocytosis-5ad652db1f4e130038c4847b.jpg)
A Definition of Endocytosis With Steps and Types

Endocytosis vesicle transport cell membrane Vector Image

Representative endocytosis mechanisms of nanoparticles. (a) Large
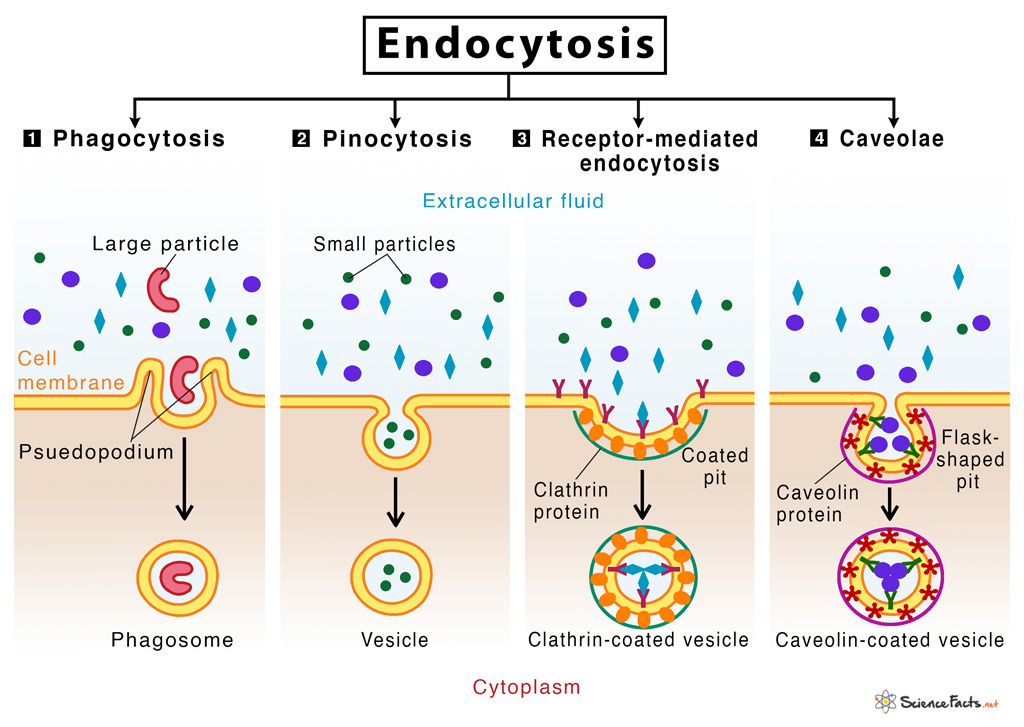
Endocytosis Definition, Types, & Examples with Diagram

Cell Biology Glossary Endocytosis Draw It to Know It
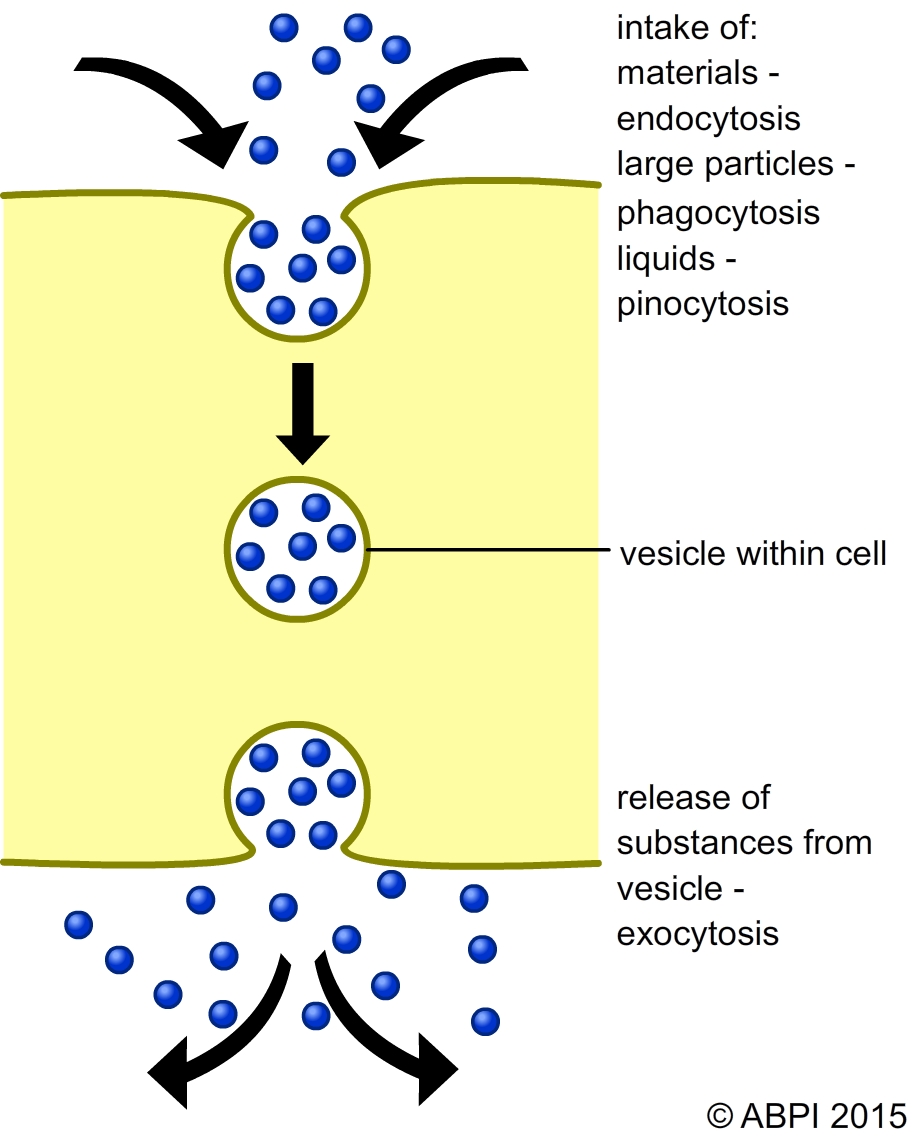
Active transport across cell membranes
It Mediates Nutrient Uptake, Guarantees Plasma Membrane Homeostasis, And Generates Intracellular Signaling Cascades.
Moreover, It Plays An Important Role In Dead Cell Clearance And Defense Against External Microbes.
Web In Endocytosis, The Cell Engulfs Some Of Its Extracellular Fluid (Ecf) Including Material Dissolved Or Suspended In It.
The Plasma Membrane Of The Cell Invaginates, Forming A Pocket Around The Target Particle.
Related Post: