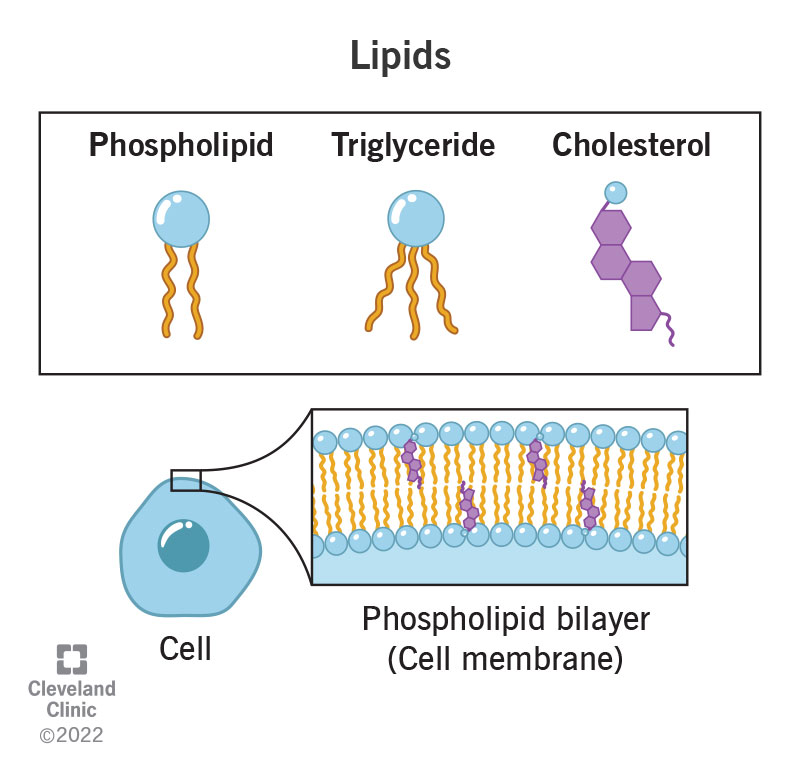
Drawing Lipids
Drawing Lipids - This molecule has many biological functions. A they are composed of nitrogenous chains. And this configuration that i've just drawn where you have a bilayer of phospholipid, of phospholipids, a phospholipid bilayer, this is how cellular membranes are constructed. Web hydrophobic, hydrophobic tails, let me draw them, draw them really fast. C they are either fats or oils. Web the different varieties of lipids have different structures, and correspondingly diverse roles in organisms. They serve as protective padding and insulation for vital organs. Lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. They are either fats or oils. It discusses the basic structure and functions of lipids such as fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, terpenes, waxes, and eicosanoids. Draw a cartoon showing how cholesterol might fit into a bilayer. Lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. Web this biochemistry video tutorial focuses on lipids. They are not soluble in water. Web the lipid maps website. Web lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Simple lipids contain a trihydric alcohol, glycerol and long chain fatty acids. Web updated on february 04, 2020 lipids are very diverse in both their respective structures and functions. High levels of niacin, an essential b vitamin, may raise the risk of heart disease by triggering inflammation and damaging blood vessels,. High levels of niacin, an essential b vitamin, may raise the risk of heart disease by triggering inflammation and damaging blood vessels, according to new research. Web revision notes on 1.2.5 lipid diagrams & properties for the aqa a level biology syllabus, written by the biology experts at save my exams. They are composed of nitrogenous chains. Web lipids are. It discusses the basic structure and functions of lipids such as fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, terpenes, waxes, and eicosanoids. These diverse compounds that make up the lipid family are so grouped because they are insoluble in water. They are a major component of the membranes of the 10 trillion cells in our bodies. Web there are many other different types. Draw a cartoon showing how cholesterol might fit into a bilayer. The simple lipids and ii. Web lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. The drawing below shows how packing is easier in saturated triglycerides, so they tend to be solid at room temperature. Web lipids have other biological functions besides energy storage. They are either fats or oils. B they are not soluble in water. Saturated triglyceride (top left) and unsaturated (top right). High levels of niacin, an essential b vitamin, may raise the risk of heart disease by triggering inflammation and damaging blood vessels, according to new research. Web revision notes on 1.2.5 lipid diagrams & properties for the aqa a. Web updated on february 04, 2020 lipids are very diverse in both their respective structures and functions. Saturated triglyceride (top left) and unsaturated (top right). C they are either fats or oils. It discusses the basic structure and functions of lipids such as fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, terpenes, waxes, and eicosanoids. Web lipids are made up of a glycerol molecule. Web lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. Web what is a lipid? There are three main types of lipids: They are composed of nitrogenous chains. Draw a cartoon showing how cholesterol might fit into a bilayer. An example, cholesterol, is shown below. They are a major component of the membranes of the 10 trillion cells in our bodies. Lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. Hydrophobic tails right over here. And this configuration. Web lipids are made up of a glycerol molecule attached to three fatty acid molecules. The simple lipids and ii. The drawing below shows how packing is easier in saturated triglycerides, so they tend to be solid at room temperature. Web lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well. Explore what are lipids, its definition, lipid structure, types and classification of lipids only at byju's. It is often found in lipid bilayers. Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, including fats, oils, steroids. A fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. An example, cholesterol, is shown below. Simple lipids contain a trihydric alcohol, glycerol and long chain fatty acids. Web lipids are a family of organic compounds that are mostly insoluble in water, meaning they do not mix well with water. They are also soluble in other organic solvents such as ether, acetone, and other lipids. Web there are many other different types of lipids. Saturated triglyceride (top left) and unsaturated (top right). Web lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Web what is a lipid? The drawing below shows how packing is easier in saturated triglycerides, so they tend to be solid at room temperature. Web draw and label a phospholipid | lipids | a level biology. Hydrophobic tails right over here. Ken bosma) fats and oils.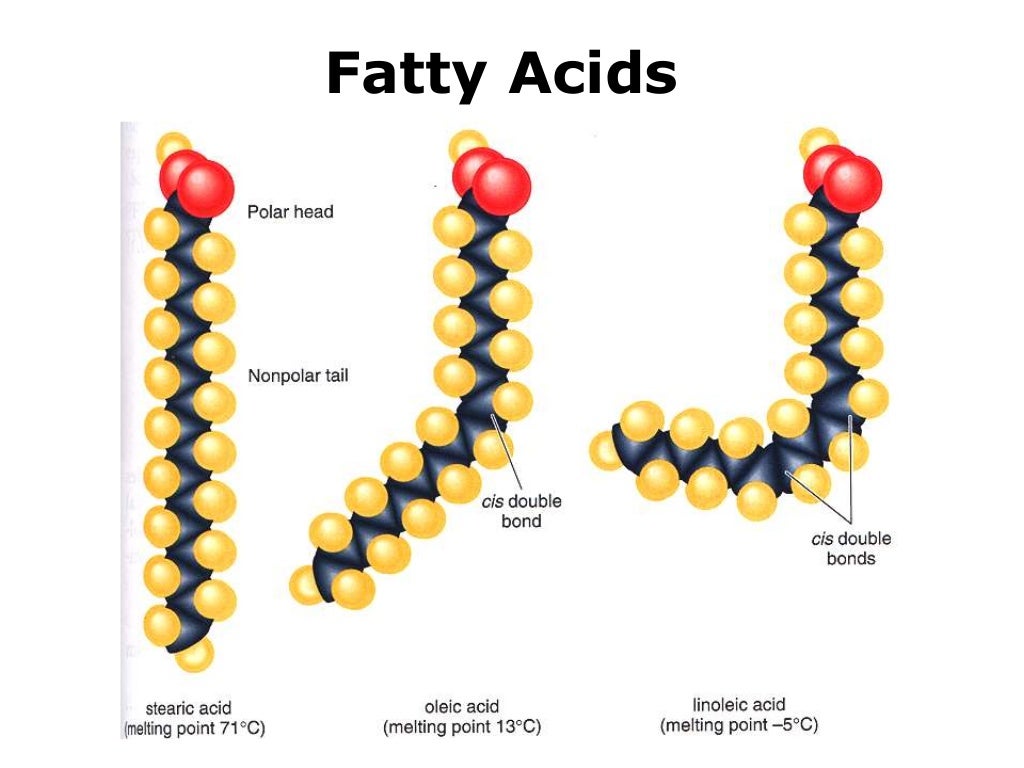
Lipids Chemistry Structure & Function

Simple Structure Of Lipids
A schematic drawing of coarsegrained model of lipid molecule. The
Chemical Structure Of Lipids
2.1.2.8 Lipids Biology LibreTexts
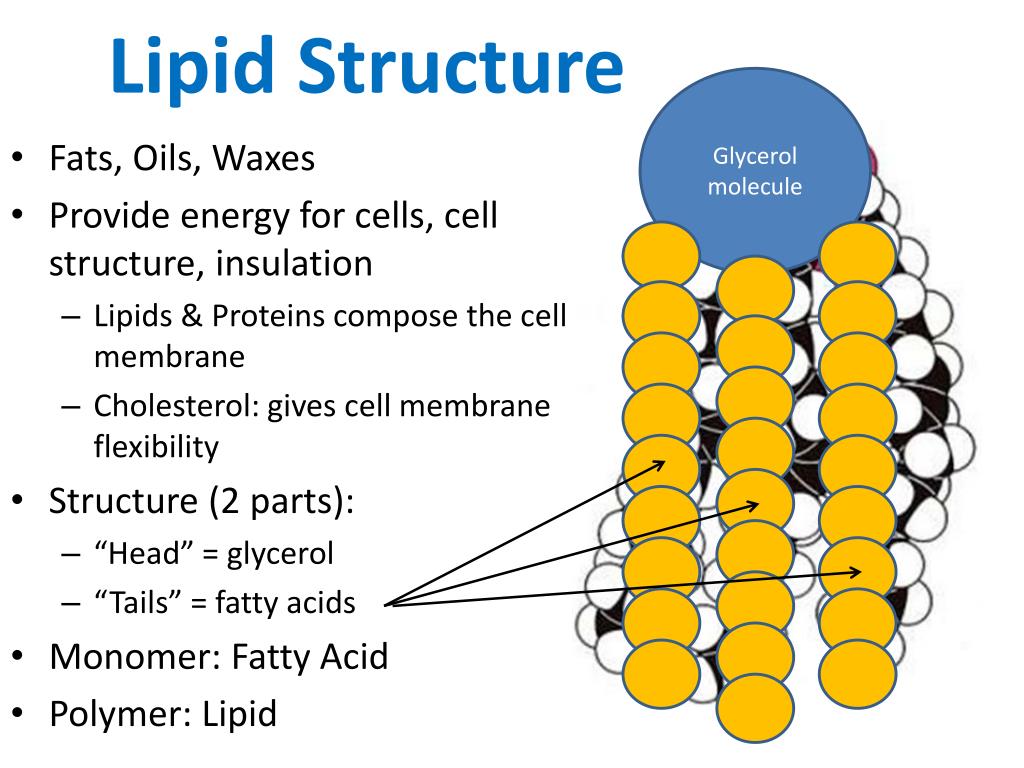
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6999007
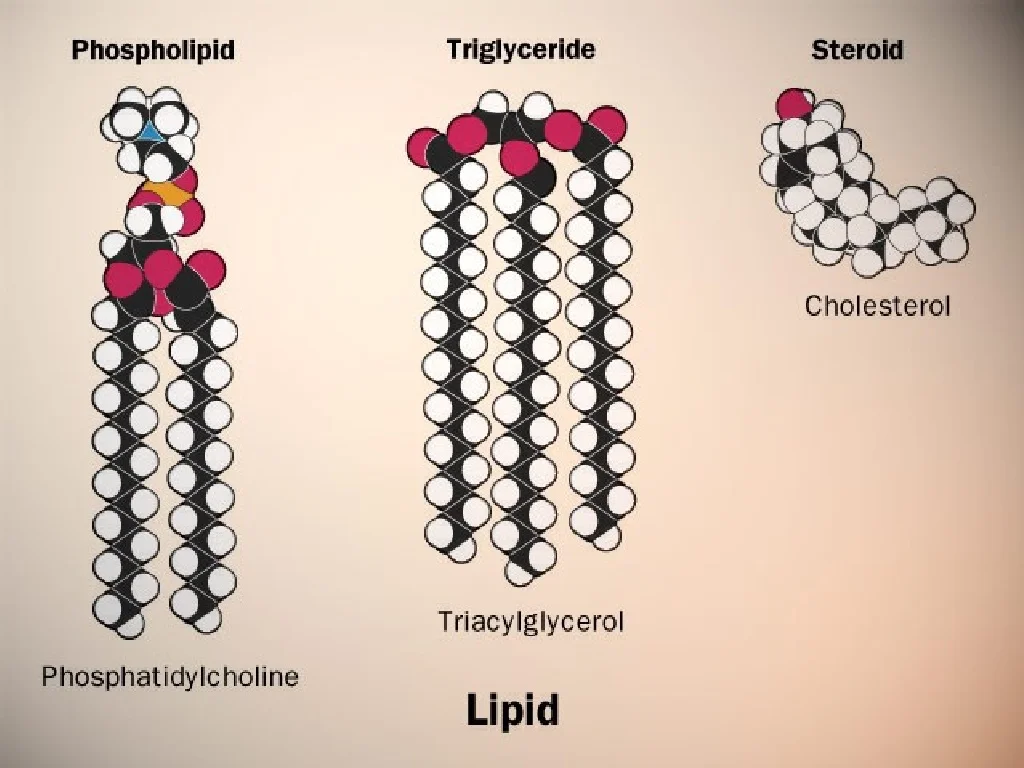
Lipids

Draw Structure Of Lipid

Lipids Biology for NonMajors I

What Is The Basic Molecular Structure Of Lipids
Such A Lipid Is Called Triglyceride.
Web The Different Varieties Of Lipids Have Different Structures, And Correspondingly Diverse Roles In Organisms.
They Are Either Fats Or Oils.
This Molecule Has Many Biological Functions.
Related Post: