Draw Longitudinal Wave
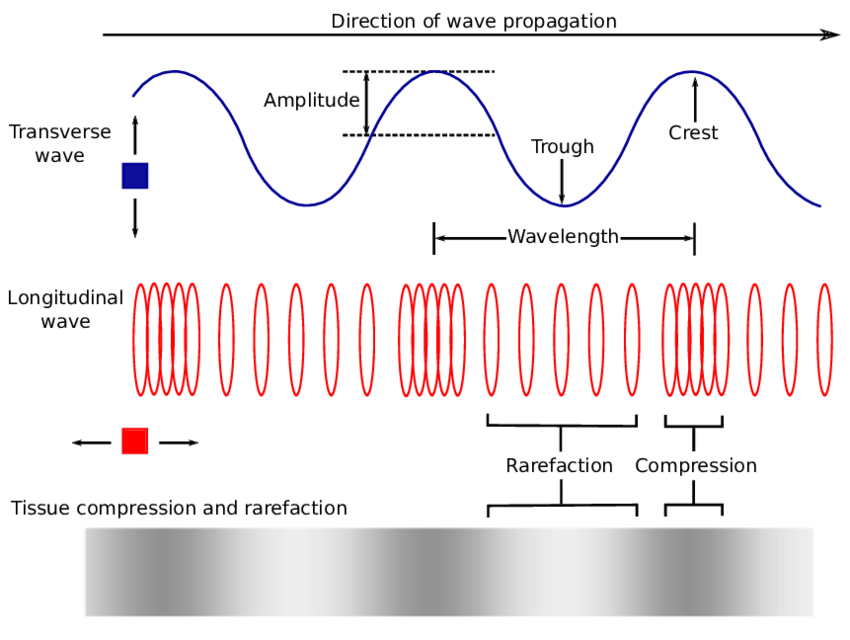
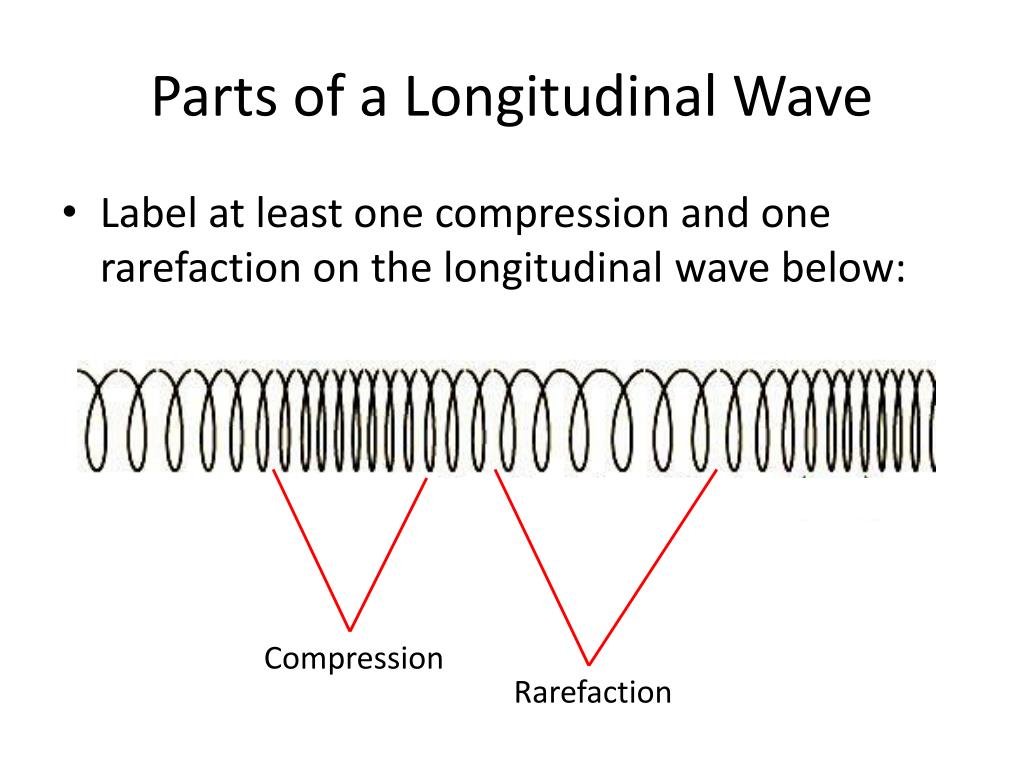
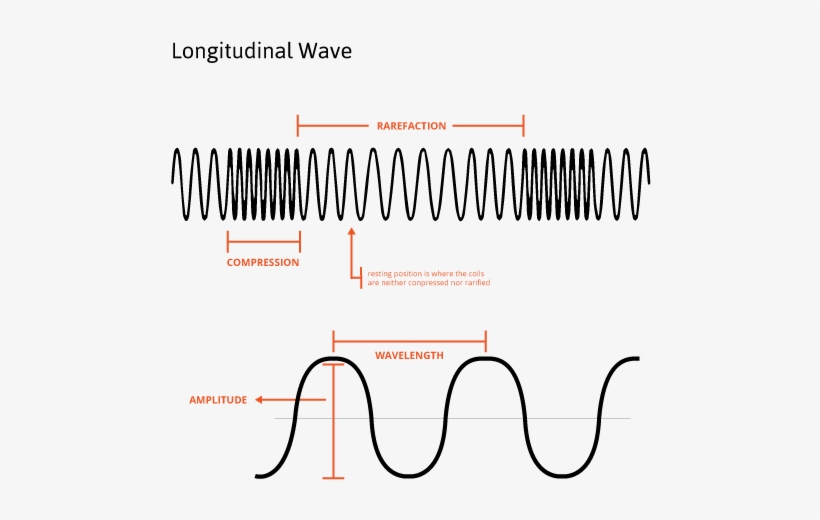
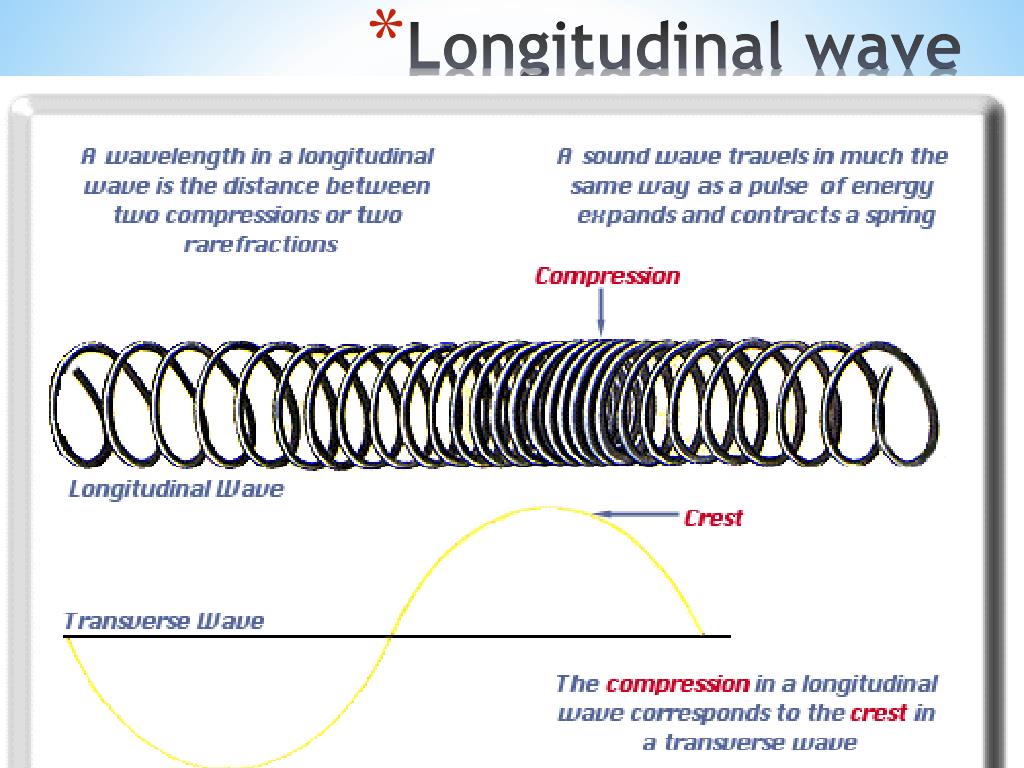
Draw Longitudinal Wave - Longitudinal waves (like sound) move in the direction of propagation, while transverse waves (like light) move perpendicular to this direction. The wave cannot be polarized or aligned: Waves may be transverse, longitudinal, or a combination of the two. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave. What you see in the picture is the wavefront progressing forward and the particles compressing and expanding in. We will also learn how to draw a transerve wave. We can make a horizontal longitudinal wave by pushing and pulling the slinky horizontally. Other examples include (some forms of) seismic waves and ultrasound. Web learn about transverse waves vs. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Diagram of a longitudinal wave. Although, transverse waves resemble physically the plots that we drew in figures 8.1.5 and 8.1.6, we represent harmonic longitudinal wave exactly the same way using sinusoidal functions. Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions. This time the displacement of a single point. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with a wide range of properties and uses. Sound waves are longitudinal waves. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. The wave can be polarized or aligned Web difference between longitudinal and transverse wave; The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. Web what is longitudinal wave? The direction of energy transfer is parallel to the direction of vibration of the. Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave. Diagram of a longitudinal wave. Other examples include (some forms of) seismic waves and ultrasound. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. The direction of energy transfer is parallel to the direction of vibration of the. It acts in two dimensions: It acts in one dimension: Web difference between longitudinal and transverse wave; What changes is the density along the line. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. This time the displacement of a single point in the medium is parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave, the defining characteristic of a longitudinally polarized wave. Web waves. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Web longitudinal waves show areas of compressions and rarefactions; What you see in the picture is the wavefront progressing forward and the particles compressing and expanding in. In a longitudinal wave, the displacement of the particle is parallel to the direction of the wave propagation. Web the most. Longitudinal waves are usually drawn as several lines to show that the wave is moving parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Web waves may be transverse or longitudinal. Web learn how to quickly label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. 2π radians = 360 degrees. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture. Web longitudinal waves and labelling wave diagrams. Waves may be transverse, longitudinal, or a combination of the two. Also, you can clean teeth using ultrasound, knock out small cancers, and obliterate kidney stones, all using ultrasound, which is sounds at. Web difference between longitudinal and transverse wave; Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. Sound waves are longitudinal waves. You could therefore draw the wave by. Other examples include (some forms of) seismic waves and ultrasound. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Longitudinal waves are waves where the displacement of the medium is in the same direction as the direction of the travelling wave. The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. Web difference between longitudinal and transverse wave; Web in a longitudinal wave the particles are displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels. What you see in the picture is. The meaning of this is that any angle can be expressed in radians as an arclength on a circle of radius 1. Other examples include (some forms of) seismic waves and ultrasound. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. The wave cannot be polarized or aligned: Study the definitions and examples of each type of wave, and examine longitudinal and. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. 2π radians = 360 degrees. It acts in two dimensions: Although, transverse waves resemble physically the plots that we drew in figures 8.1.5 and 8.1.6, we represent harmonic longitudinal wave exactly the same way using sinusoidal functions. Longitudinal waves are sometimes called compression waves or compressional waves, and transverse waves are sometimes called shear waves. A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length, followed by a stretching; Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Web waves may be transverse or longitudinal. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with a wide range of properties and uses. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport.
Longitudinal wave Physics, Sound & Wave Motion Britannica

Oscillations and Waves online presentation
Wave, its types and characteristics Online Science Notes
PPT Chapter 17 Mechanical Waves & Sound PowerPoint Presentation ID

Transverse & Longitudinal Waves Definition, Differences & Examples
Draw A Diagram On The Board Of A Longitudinal Wave Longitudinal Wave
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329

Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams YouTube

Waves Class 11 Notes, Formulas, NCERT, For NEET Leverage Edu

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and
The Medium Moves In The Same Direction Of The Wave:
We Can Make A Horizontal Longitudinal Wave By Pushing And Pulling The Slinky Horizontally.
Web Longitudinal Waves Show Areas Of Compressions And Rarefactions;
What Changes Is The Density Along The Line.
Related Post: